
Many infections do not cause symptoms in healthy people. The immune system suppresses the virus activity and, consequently, the person becomes the carrier of the infection. When the transmission of this pathogen to the other, occurs even if you have a wellness clinic, because that virus particles contained in the fluids of the sick. Hidden during infection may be the main cause of the considerable spread of the disease: patients in a timely manner, do not go out of the survey and continue to spread it to other people unconsciously.
The human papilloma virus (hpv) can appoint a perfect example hidden by the infectious agent. The majority of the people it infects at least one type of hpv throughout life, however, the clinical manifestations of the disease occur not in all cases. To the complications of the infection, doctors have a greater risk of formation of a malignant tumor. By doing so, patients suffering from immunodeficiency syndrome, often occurs it is a negative consequence of the disease. Topical medications help suppress the symptoms of the hpv infection. Vaccination is also recommended timely.
Read more about the disease
The human papilloma virus is the cause of the infections that attack skin and mucous membranes of the organs. The main manifestation of the disease is the growth of the tumors in the face, the genitals, the oral cavity and throat. In some cases, acuminate papilloma are formed in the effects of nonspecific sites, such as the skin of the upper and lower limbs. The location of the warts depends on the type of hpv. The majority of people, the infection leads to the hidden transport of the infection, however, the decrease in the immunity the virus starts to express its virulence. In some cases, the immunocompetent cells self-destroy pathogen within 3-6 months after their invasion in the body.
The hpv infection is the most common form of the disease, the infection of sexually transmitted. This indicator can explain the meanings of the high virulence asymptomatic of the virus and the pathology is of the most people. The use of condoms cannot always prevent transmission, so that the patient can continue shedding the virus even when protected by sexual contact. At the same time, the experts have developed effective vaccines to prevent the development of oncogenic forms of hpv. Immunization was shown to the girls in the adolescence, as the protection against viruses should inculcate before the first sexual contact.
The characteristics of the virus
The human papilloma virus is dna-containing pathogen. Unlike bacteria and other micro-organisms, viruses can exert their activity only after the deployment in the cage and the insertion of their own genetic information in the nucleus. After this affected the cell begins to synthesize the necessary proteins for the assembly of the viral particles. Almost all the representatives of the family human attack a single type of organisms, and the hpv infection can only occur in humans.
Scientists know more than 600 strains (types) for the human papilloma virus, which differ from genetic information. 40 types of hpv cause different forms of the defeat of the mucous membranes and the skin. When this potential clinical importance is the classification of degree of oncogenetic strains. Thus, the cancer of cervix in women most frequently occurs when the invasion of hpv 16 and 18 types. These infectious agents do not always manifest changes in the skin.
Hpv infects basal layer of epithelial cells. The pathogen may be in the form of episome, are not associated with the cellular dna, or in an integrated way, related to the genome of the cell. It is built-in virus and produces proteins necessary and to produce the clinical manifestations of the disease. The livelihoods of hpv in the body is not the direct cause of the malignancy of the degeneration of the tissues, however, be a carrier of the virus increases the risk of the risk factors of cancer.
Forms of transmission
The virus contains in the basal cells of the epithelium, so that any micro injuries of the skin and of the mucous membranes increase the risk of infection. In most cases, hpv is spread during sexual intercourse-vaginal, anal or lingual sexual contact. The condom can protect only a part of the surface of the skin, however, the viral particles can penetrate into the body through other garments. The presence of genital warts, predisposes to the transmission of a pathogen, but externally the skin intact half of the disease is also a source of hpv.
Other routes of transmission
- The infection in the baby during delivery. The children often produce lesions of the respiratory tract
- Independent of the transmission of an area of the body to another
- The total use of toiletries, including razor, toothbrushes and towels
- A blood transfusion. Recent studies have confirmed the possibility of transfusion of infection.
- Surgical interventions in conditions not disinfected
Despite the variety of causes of the invasion of the virus, only the gender of the route of hpv infection has clinical significance. Other sources of infection are characterized by a low risk of spread of the pathogen.
Risk factors
In addition to direct, to the modes of transmission of hpv, you should also take into account the role of risk factors. It is the characteristics of the image of the life of the person and certain physical states.
Major risk factors for infection
- A large number of sexual partners. Even with safe sex active sex life, sooner or later leads to infection.
- Age. Genital warts in the majority of cases are detected in adolescents and young patients, while the condylomata of the oral cavity and the respiratory system are characteristic of children.
- A weakened immune system. Patients suffering from hiv infection or acquired immunodeficiency, are at high risk of virus invasion. Also hpv and more evident symptomatically after an organ transplant.
- The damage of the skin and mucous membranes. Micro injuries that facilitate the penetration of the virus in the basal cell layer of epithelial cells.
- Smoking and alcoholism. Bad habits weaken the activity of the immunity.
- Urinary of the infection.
In addition, in the group of risk of infection include pregnant women. It should be remembered that the elimination of the predisposing factors to the disease is an effective preventive for the tactics.
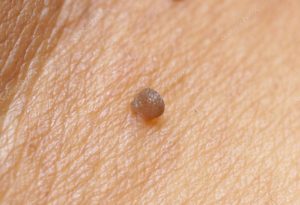
Clinical evolution
The incubation period prior to the symptomatic manifestations of the disease, can last for months or not. The immunocompetent patients during this time, the body can destroy the infection, however, spontaneous clearance of a pathogen is not always the case. A person can be at the same time is infected with multiple strains of the virus. The signs of the hpv infection, which occur when the impact of unfavorable factors, weaken the immune defense of tissues. Due to the recurring of the current warts periodically disappear and then form again. Cancer is one of the complications of the infection can evolve over several tens of years.
The possible consequences of the disease:
- The carcinoma of the uterine cervix – malignant epithelial tissue. This type of cancer associated only with the human papilloma virus. When vaccination timely risk cancer decreases.
- Squamous cell Carcinoma anal. This complication can occur in both men and women. Early symptoms of anal cancer include bleeding and itching in the skin.
- Violation of urination due to obstruction of the urethra the warts.
- Malicious rebirth of warts in the area of the throat and the oral cavity.
The cancer of neck of uterus is one of the most frequent causes of death in women. Because it is a disease related to the virus produce an invasion, it is necessary to regulate the pace of polls with the gynecologist. Modern vaccines protect women from these oncogenic types of hpv.
The diagnosis
The inspection of the condylomata are engaged gynecologists, urologists, venereologists and dermatologists. During the reception, the doctor will ask the patient about the complaints, will bring anamnesticheskie the data and will carry out an inspection of the skin of the entities. Normally, the manifestations of hpv are easily identified, however, it is necessary to rule out other diseases. To this end, the specialist will prescribe and instrumental laboratory.
Methods of diagnosis:
- Instrumentation for the inspection of the vagina and the cervix (colposcopy). This study is mandatory for the screening of cervical carcinoma. During the examination, the doctor can detect multiple papilloma and areas epitelialnoy of dysplasia.
- Biopsy – obtaining fabric materials in the area of the skin or of the mucous membranes of the changes. Cytologic Screening of the sample allows to detect malignant cells.
- Polymerase chain reaction – detection of viral particles of HPV in the body. The application of this test gives the physician the possibility to determine the strain of pathogen and viral load.
- Digene-test high precision of the detection of the dna of oncogenic strains of the human papilloma virus. The study is used as a screening program.
The pharmacological treatment
Produced by the medicines against the hpv, to allow only resolve the symptoms of the disease and prevent the malignancy of the tissues. Complete virus removal with the help of the drug therapy is not possible. Oral, and topical funds are allocated in the case of high-risk cancer, immunodeficiency and other conditions of the state. If the virus does not manifest itself in the external changes, enough general prevention measures.
Possible destination
- The salicylic acid to remove warts. Not used for the treatment of the skin of the face and genitals.
- Creams and ointments containing immunomodulators of the tool.
- Podofilox – ointment with cytotoxic action. The path of medicines affected of the skin leads to the destruction of the pathogens of the elements.
- Trihloruksusnaya acid for cauterization chemistry general and of genital warts. Can cause local section of expression.
The drugs should only be used under control treatments. After the removal of warts of hpv, the infection can manifest itself in new and even spread to other areas.
The surgical treatment
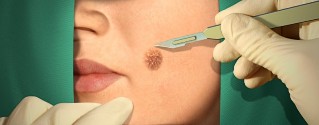
The doctor may suggest the surgical patient and minimally invasive methods of removal of warts. In general, these techniques do not cause complications, however, in the first few days after surgery bleeding may occur from the tissues.
Types of intervention:
- normal, the surgical removal;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen, with the follow-up of the destruction of the tissues;
- electric coagulation;
- the removal of papillomas with a laser.;
- the use of radiowave "the knife".
All procedures performed under local anesthesia. The specialist will require the more secure method of the treatment of genital warts.
Prognosis
During the human papillomavirus infection depends on the immune status of the patient and specific for the strain of the virus. In approximately 30% of the population occurs the spontaneous clearance of a pathogen, subject to the active immunity. Symptomatically, the disease appears often in pregnant women, children, the elderly and patients with immunodeficiencies.
For the hpv, which is a recurring feature of the current. Have formed papilloma may gradually disappear, or distributed in adjacent areas of the skin. Oncogenic strains of virus often affecting the mucous membrane of the neck of the uterus, and occurs epithelial dysplasia reinforces the effect of the factors of risk of malignancy of the tissue degeneration, such as smoking and the use of oral contraceptives. The tumor can take 10 to 20 years after the invasion of the virus in the body.
The prevention of the
The most reliable method of prevention is a first immunization. A hpv vaccine", which contains the viral proteins and the accessories, it is effective against hpv 6, 11, 16 and 18 types. If vaccination is performed at an early age at first sexual intercourse, the risk of subsequent development of cancer of the cervix in women is less than 1%.
More prevention:
- the use of condoms;
- sex only with partners;
- scrupulous personal hygiene;
- examination a physical at least once a year.























